Introduction
In this module, we will install a virtual environment in your computer, and explore the use of Linux.
What are virtual machines?
Virtual machines are like a computer within your computer.
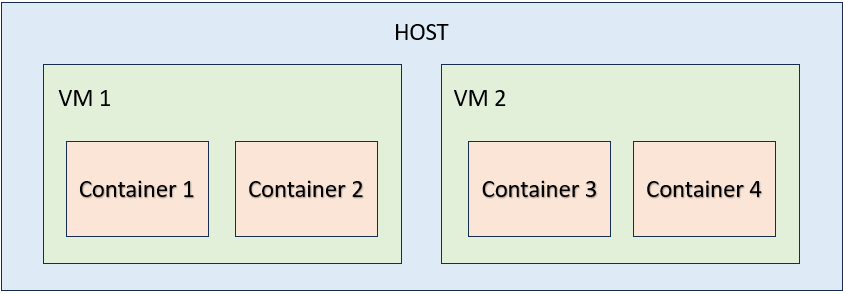
What Guest Operating System can you run inside your main computer?
- Windows
- Linux
- Android
For MacOS, it is possible, but it is likely illegal. Apple only allows for MacOS to be run on MAC hardware. see https://www.apple.com/legal/sla/docs/macOSMonterey.pdf for more details.
As of this writing, computers with Apple's M series chips can be used in virtual machines, however, the ISO file that is used need to support the ARM architecture.c
For IT professionals in general, we will run any OS systems in a virtual environment based on the task at hand..
Installing VirtualBox
VirtualBox is a free software provided by Oracle. We will use VirtualBox for this content. You may use other virtual machine software such as VMWare if you choose to.
Download the software from the official virtualbox source. https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads.
We only need the base software, but feel free to install the VirtualBox Extension Pack for capabilities if you need them.
Proceed to install VirtualBox on your computer.
Hardware requirements
Make sure your computer has enough RAM, and discspace, as the virtual environment will share the resources of your host OS.
Selecting your Guest OS
Ubuntu is a popular general-purpose Linux distribution.
This tutorial will take you through the process of creating a fresh install from an image file.
If you have trouble with the installation process for Ubuntu
You may use Kali Linux instead.
You can download the OVA file from this link https://www.kali.org/get-kali/#kali-virtual-machines.
Choose the download for VirtualBox(64-bit).
Once done, simply double click on the OVA file for VirtualBox to import the virtual machine.
Downloading Ubuntu
Ubuntu is a well-known distro of Linux. It is a Linux distribution with many useful tools installed for us so that we do not have to.
Download the Ubuntu Desktop ISO file from this link (https://ubuntu.com/#download).
An ISO file is an image file, much like a CD/DVD for offline OS installation. We will use this image file to create a fresh install of Ubuntu in a virtual machine.
Other OSes can also be installed this way.
Installing Ubuntu
Open the VirtualBox software. Click on the "New" button at the top to start.
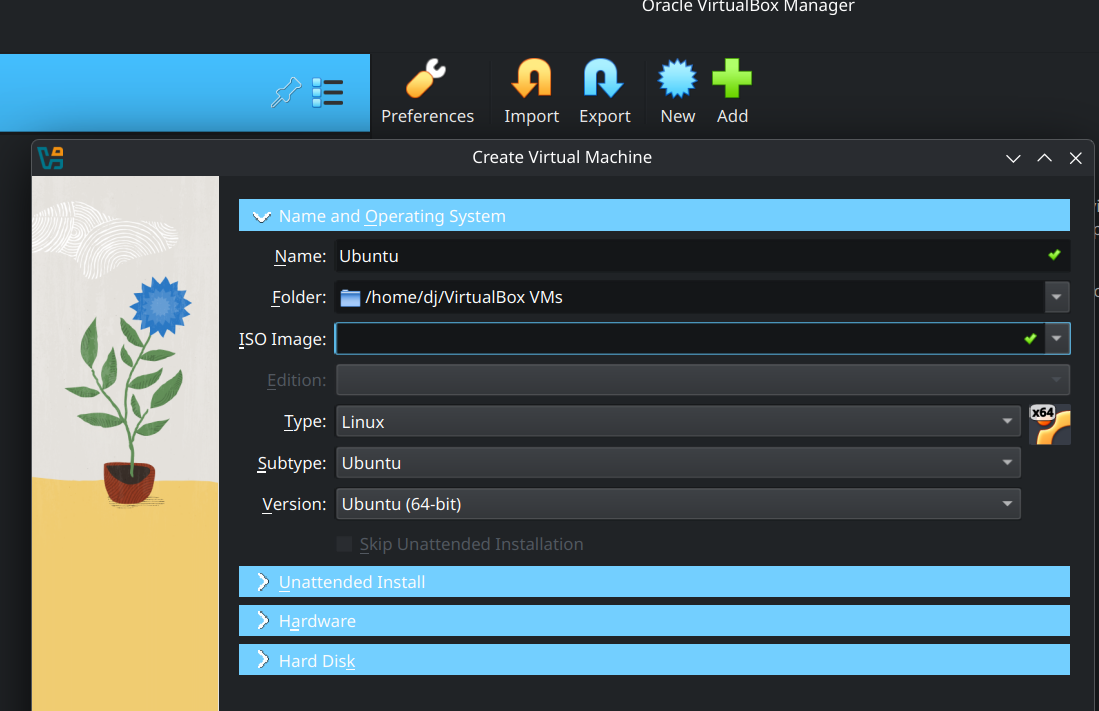
Choose the folder where you want to install the virtual machine in.
This will take up space. Ensure that it is in a drive that has enough space. You can use your C drive or D drives as long as there is enough space. SDD drives will perform better, but there are no problems in using HDD drives for your VM.
Choose Operating System
Choose Linux and choose Ubuntu 64-bit as follows.
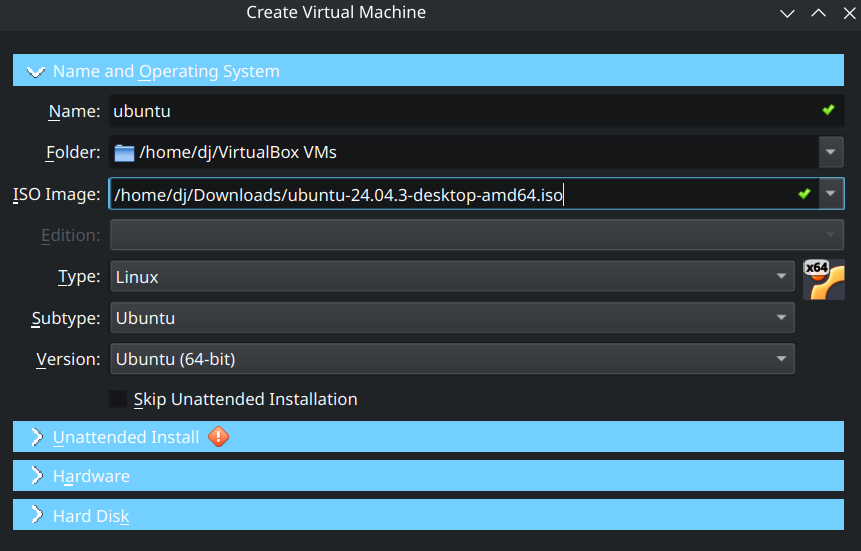
If you have problems with the unattended installation, skip it and install the OS manually once the virtual machine is booted.
Choose amount of RAM to give the machine
Choose the amount of RAM. Linux generally uses less RAM, so the default suggestion of 1024mb of RAM might be enough.
Here, I chose 2 gigabytes(which is 2048 megabytes) of RAM, and 2 CPU cores.
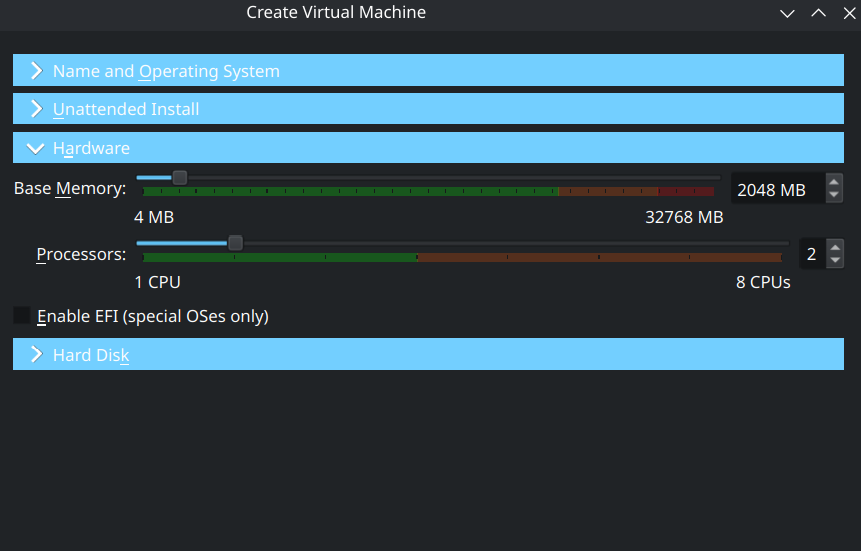
This is to dedicate resources from the host machine to the virtual machine.
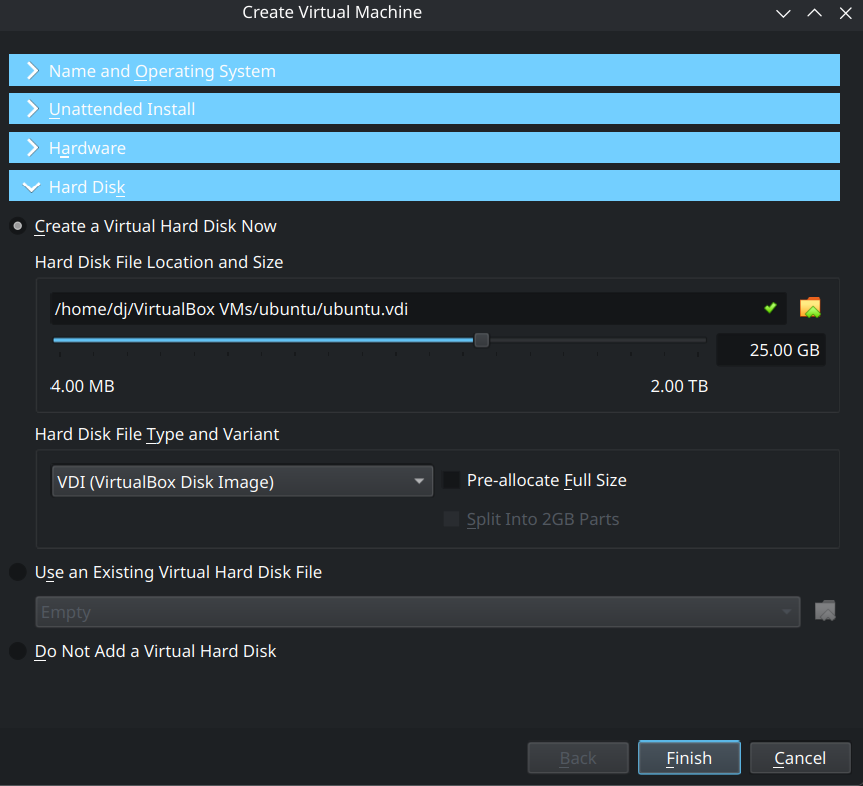
Choose the virtual hard disk
We do not have existing hard disks. Choose the "Create a virtual hard disk now" option.
Choose the type of virtual hard disk
Since we are solely using VirtualBox, choose the VDI option.
Choose the type of disk allocation
For example, if we want our virtual machine to have 100GB of space.
Dynamically allocated will mean that space is only taken up as it is used. I.e. your actual space used on your HOST machine can be 10GB only. As you install or download more things, the space used will slowly increase accordingly.
With this option, you are able to use your computer more efficiently.
Fixed size
Fixed size will simply block off and reserve the 100GB of space immediately for the virtual machine. Even if you have nothing much in your virtual computer, it will take up 100GB of space on your host computer.
Generally, using "Dynamically allocated" is good enough.
Choose the size of virtual hard disk
The default size suggested is 25GB. You may increase it if you wish to.
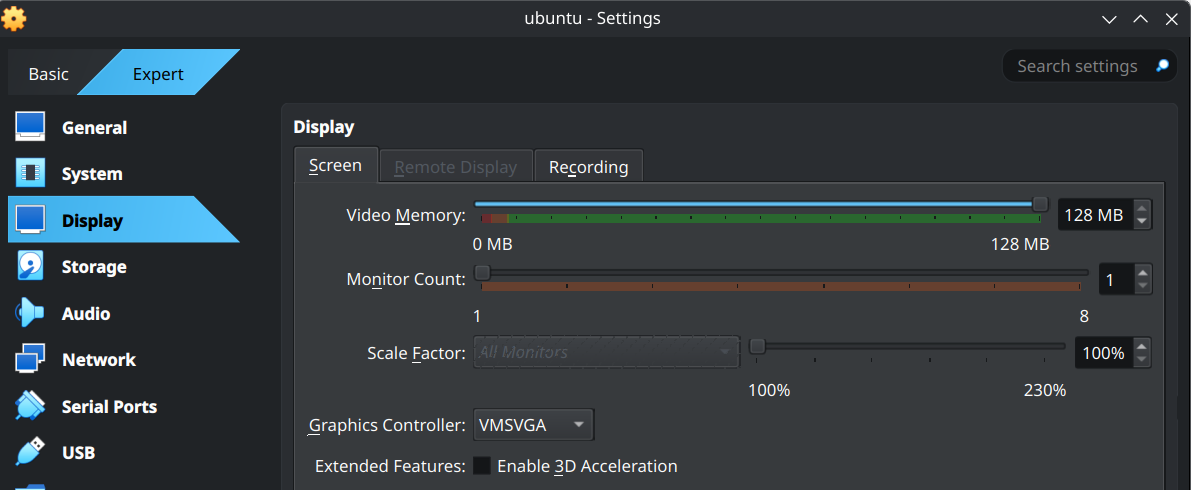
Video Memory
After clicking on finish, you will see the VM icon on the sidebar

Go in to settings > display > video memory
Start the machine
Click on start button.
The virtual machine will start, follow the onscreen instructions to install Ubuntu.
If you need more detailed instructions, you may refer to https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/how-to-install-ubuntu-on-virtualbox.